Just like English lets us understand the conversations happening in the English speaking countries, or how Japanese allows us to follow the conversations happening in Japan, understanding blockchain also requires learning its very own language!
Worry not! In this blog post, we will explain the most important blockchain terms that you need to know without any complex phrases. And yes, I promise it will be both educational and entertaining so grab your virtual passport because we are about to go on an adventure… Just kidding, I mean we will take you through it step by step!
Blockchain
Okay, we have talked about this term a lot in our previous posts so I will just quickly bring it up again to refresh your memory. If this is your first time visiting blockchaintreat.com and you have not read our introduction to blockchain, be sure to check it out here: What is Blockchain? A Beginner’s Guide
Block
Now let us dive deep into the blocks that is termed as building blocks of the blockchain (pun intended!). A block in simple terms is a container used to store data. Every block contains information on a particular transaction such as who sent what to whom and when the transaction occurred.
Every block also consists of additional information as follows:
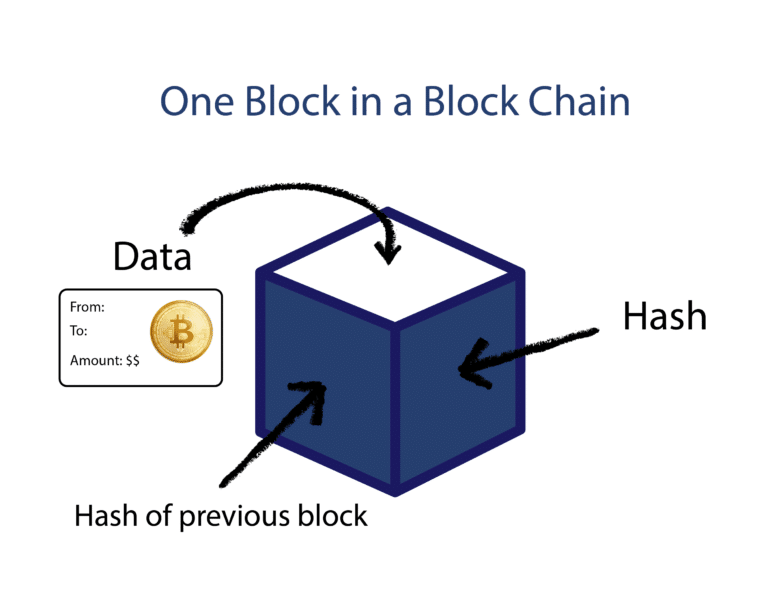
- Data: This refers to the relevant pieces of information pertaining to the transaction (like who sent the digital cat to whom).
- Hash: Think of it as a code that refers to the block and serves to uniquely identify it. It is akin to a fingerprint of the block.
- Previous Block’s Hash: This works as another reference while enabling the blocks to stay chained together.
Example: Think of a block as an entry page in a journal in which you log key details pertaining to an event in this case the transaction as the event.
Chain
This one’s easy! A chain is nothing but a combination of series of blocks joined together. Each block references the previous block thus making it almost impossible to change.
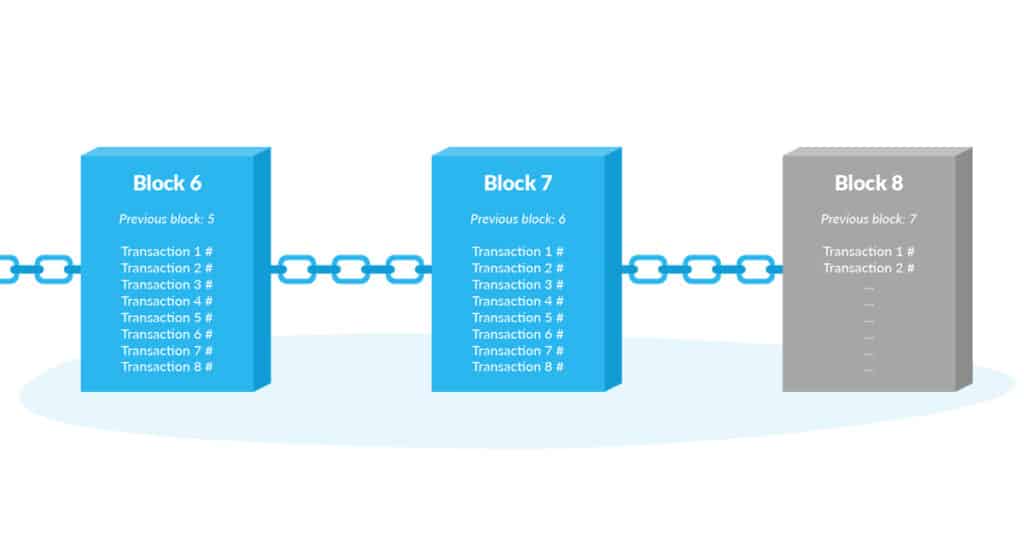
You cannot substitute a single block without the intention of substituting the subsequent blocks which will break the chain. This factor is what makes blockchain highly secure.
Example: A chain resembles a sequence of paperclips, each connected to its predecessor. If one of the clips is removed, the integrity of the chain is completely lost.
Node
A node refers to a single computer and is any member of the blockchain network. Data is never lost even if one node ceases to function, for every node contains a copy of the entire blockchain.
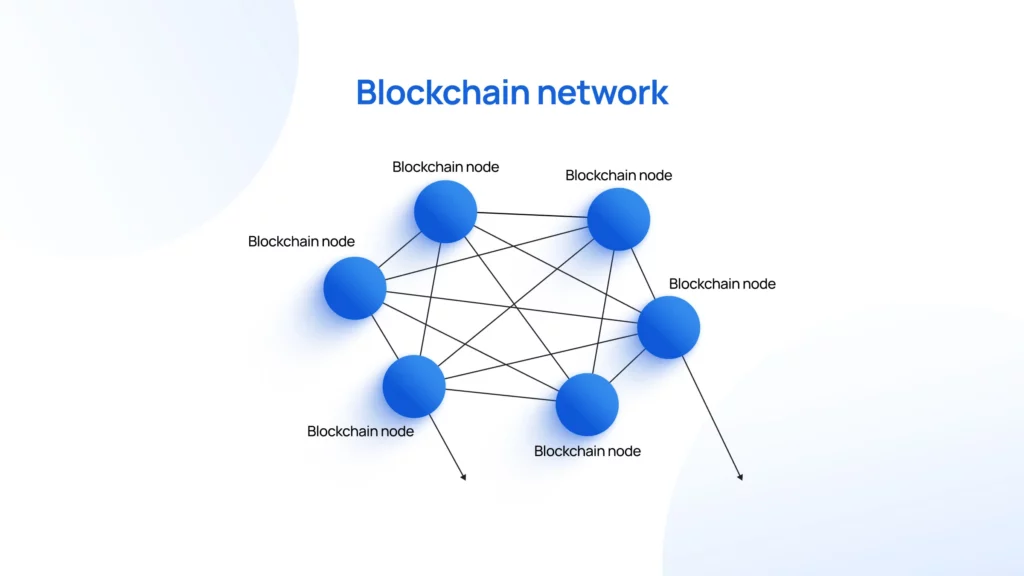
Each node is similar to an employee in a large organization. They all work in parallel, maintaining their individual copies of the blockchain ledger. Nodes also partake in verifying and validating new transactions to ascertain their authenticity.
Example: A node is similar to a person in a classroom that possesses the class notes. This individual can lend their notes to any students who did not attend class.
Decentralization
This concept means there is no single authority such as a person, organization, or corporation controlling the blockchain. The power is distributed among the constituents of nodes. A decentralized network does not have a single point of control and this means there is no single point of failure. For example, in a group project, everyone pitches in. So no one can sit back and relax while doing no work at all.
Example: If a dinner is hosted where all the guests are expected to bring food, then it is referred to as a potluck dinner. If any one person does not arrive, the meal can still be enjoyed by other people.
Cryptocurrency

These days, I am certain that you have encountered businesses that deal with Bitcoin, Ethereum and so forth. Such currencies are known as cryptocurrencies. Blockchain technology is used for monitoring and recording transactions. Cryptocurrency is a form of digital currency that is not regulated or monitored by any government or financial institution.
This is akin to having currency in a video game—for instance, instead of being restricted to the bounds of a game world, this money can be utilized in the real world.
For reference, cryptocurrency is a form of digital gold unlike traditional gold that is kept in a vault, instead it is stored in an online wallet.
Wallet

You keep your cryptocurrency in a digital wallet. Just like your physical wallet contains bills and coins, your digital wallet stores your digital currency. There are wallets in the form of phone applications and even hardware devices. Some wallets are online and some are offline, described as hot wallets and cold wallets respectively.
Example: A wallet is like a purse, but instead of holding paper bills, it holds your Bitcoin or Ethereum.
Mining
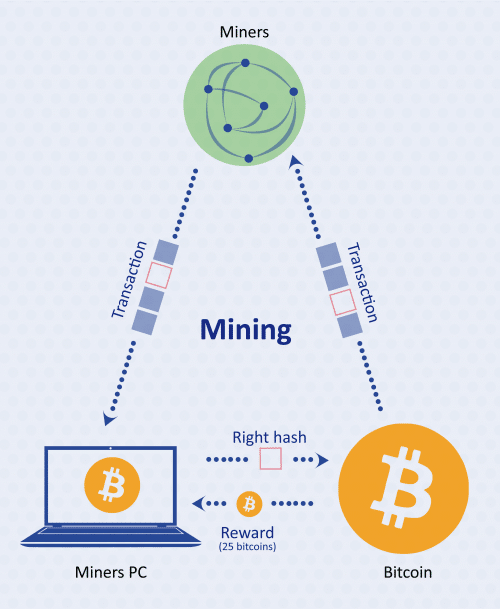
In mining, miners validate transactions, and document them on the blockchain by solving a blockchain puzzle. The miner that solves the puzzle first is rewarded with cryptocurrency, such as Bitcoin.
Mining is the method of adding new coins into circulation. But don’t worry, you’ll never need a pickaxe or hardhat for this kind of mining, instead, all you’ll need is a good computer!
Example: Mining is like solving an extremely perplexing math equation. If the answer is correct, then there is a reward up for grabs.
Smart Contracts
A smart contract is a self validating contract with the terms of the agreement being part of the software. The contract is executed when specific provisions of the contract is met. This means that neither a lawyer nor a bank needs to impose the rules.

It’s akin to configuring a self-service vending machine. You place some money into it (the condition) and the machine dispenses the snack you selected (the result).
Example: A smart contract is like an online order form where the moment and you press the “buy” button, your payment goes through and the item is shipped directly to you.
Fork
A fork occurs when there is an update or modification in the protocol of the blockchain. It is like making alterations to the rules of a game in the middle of it being played. There are temporary forks, which are called soft forks, as well as permanent ones, known as hard forks.
Hard forks are the reasons behind the emergence of new chains branching out from the original chain, causing two blockchains to exist simultatenously. It’s like a diverging road that leads to different destinations. The above image is an example of a hard fork where Ethereum Classic (ETC) was hard forked from Ethereum (ETH).
Example: A fork is like when a group of friends can’t make up their mind on what restaurant to eat, so some go to a pizza place while others go to a mexican restaurant.
Token
Tokens are digital assets built on the core functionality of blockchains which enables them to carry almost anything from voting rights to a portion of a digital asset or even a collectible. They are also used for pledges, gifting, and even participation in events.
Example: A token is like a souvenir or a memento that you keep from every event. It carries a lot of memories but does not serve a purpose other than that.
Consensus Mechanism

In essence, what is a consensus mechanism? This is the method used by a blockchain network to come to an agreement on which transactions are valid. There are numerous types of consensus mechanisms, some of which include: Proof of Work (PoW), Proof od Stake (PoS), Proof of Capacity (PoC), Proof of Activity (PoA), Proof of History (PoH), and even Proof of Liquidity (PoL). These protocols guarantee that each participant in the network has the same information and that no foul play is occurring. (If you’re getting lost with these mechanism terms, don’t worry, I will go over it in other posts).
For example, think of a voting system where a consensus mechanism is a set of individuals who take part in the voting and have to reach a collective decision which all will agree to before it is passed.
Wrapping Up
You now know how some of the major cornerstone blockchain terms work, and managed to break it down to the best of my ability. Fathoming and wielding these concepts will serve you well whether you plan to engage with cryptocurrency, NFTs, or just get a better insight behind how a blockchain operates. Understanding the terminology is a first step towards blockchain literacy.
A lot of these terms will make more sense as you can continue on your blockchain journey. There’s no harm in navigating deeper into this world. Better yet, you might be the next person breaking down blockchain concepts for a loved one.
Eager to discover more? Please wait for my subsequent post where I will discuss ‘Blockchain fundamentals: Decentralization and Trust’, where we will understand how these key pillars of Blockchain make it revolutionary. Until then! 🚀
Previous Post: What is Blockchain? A Beginner’s Guide
Next Post: Blockchain Basics: 2 Key Pillars – Decentralization and Trust
